Introduction to the Blue Jay bird
The Blue Jay (Cyanocitta cristata) is one of the most recognizable and intelligent birds in North America. With its striking blue feathers, loud calls, and complex social behavior, the Blue Jay has fascinated bird watchers and nature enthusiasts for centuries. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about this beautiful bird, including Blue Jay facts, its natural habitat, diet, mating behavior, and how to attract Blue Jays to your backyard.
What is a Blue Jay?
The Blue Jay is a passerine bird in the family Corvidae, which also includes crows, ravens, and magpies. Native to eastern and central North America, the Blue Jay is known for its vibrant blue plumage, white chest, and distinctive crest. Adult Blue Jays typically measure about 9–12 inches (22–30 cm) in length and have a wingspan of 13–17 inches (34–43 cm).
Despite their name, Blue Jays are not actually blue. The blue appearance is caused by the scattering of light due to the microscopic structure of their feathers — a phenomenon known as structural coloration.

Blue Jay Habitat
Blue Jays are highly adaptable birds that thrive in a variety of environments. Their preferred habitats include:
- Deciduous and mixed forests
- Wooded suburban and urban areas
- Parks and gardens with tall trees
- Edges of woodlands and open clearings
While most Blue Jays are found in the eastern United States and southern Canada, some populations are expanding westward. During winter, some Blue Jays migrate south, but migration patterns can be unpredictable and vary greatly among individuals.

Blue Jay Behavior
One of the most interesting Blue Jay facts is that they are incredibly intelligent and social. Blue Jays live in small family groups, and during fall and winter, they often form loose flocks.
Here are a few key behavioral traits:
- Vocal Mimicry: Blue Jays are known to mimic the calls of hawks such as the Red-shouldered Hawk and Red-tailed Hawk. This may help them scare off other birds from food sources or alert their group to danger.
- Caching Food: Blue Jays store food items like acorns, nuts, and seeds in various hiding spots to retrieve later. This behavior contributes significantly to forest regeneration, as some cached seeds germinate and grow into new trees.
- Territorial Defense: Blue Jays are known for their aggressive behavior when defending their territory, especially during nesting season. They will chase away larger birds, predators, and even humans who get too close.

Blue Jay Diet
The Blue Jay’s diet is omnivorous and highly varied. These birds are opportunistic feeders and consume both plant and animal matter. Their diet includes:
- Nuts and seeds: Particularly fond of acorns, sunflower seeds, and peanuts.
- Fruits and berries: Such as blackberries, elderberries, and grapes.
- Insects: Grasshoppers, beetles, caterpillars, and occasionally spiders.
- Bird eggs and nestlings: While controversial, Blue Jays have been known to raid nests, although this behavior is not as common as often assumed.
- Human food scraps: In urban areas, they may scavenge from garbage or eat from feeders.
If you want to attract Blue Jays to your yard, offer food like unsalted peanuts, sunflower seeds, and suet in a large, open feeder.

Blue Jay Nesting and Mating
Blue Jays are monogamous and typically mate for life. The breeding season begins in late March and can last through July. Here’s a closer look at their nesting habits:
- Nest location: Nests are built in trees or tall shrubs, usually between 10 and 25 feet off the ground.
- Nest construction: Both male and female Blue Jays participate in building the nest using twigs, grass, and mud.
- Eggs and incubation: A female lays 3–7 eggs and incubates them for about 16–18 days. During this period, the male feeds the female.
- Raising chicks: After hatching, both parents feed the chicks for 17–21 days until they fledge (leave the nest).
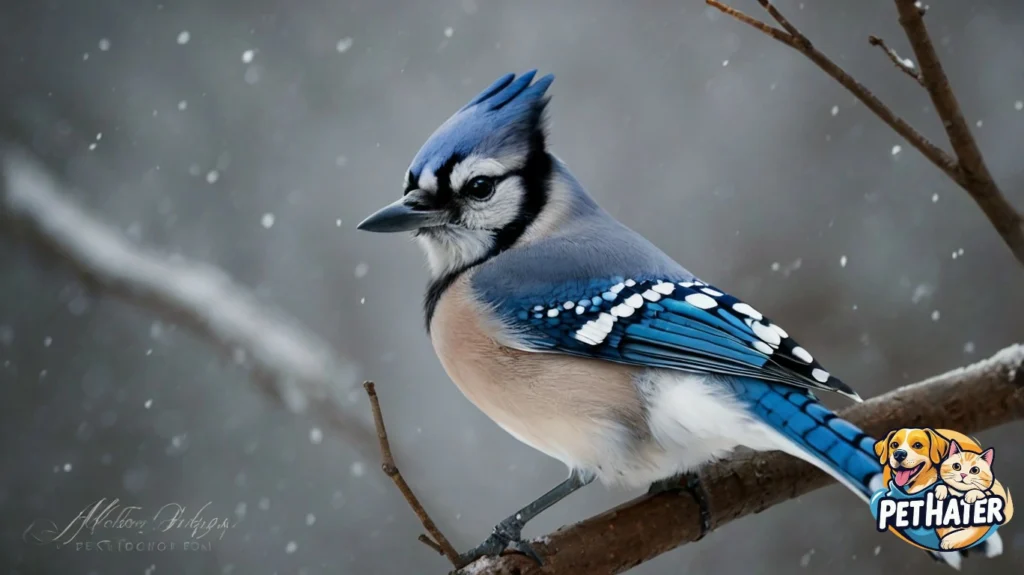

Blue Jay Calls and Communication
Blue Jays are among the most vocal birds in North America. Their sounds range from harsh screams to melodious whistles. They use vocalizations for various purposes, including:
- Alarms: Warning others of predators or intruders
- Mimicry: Copying hawk calls to deter competitors
- Social bonding: Gentle calls between mates or flock members
Their most common call is a loud, descending “jay-jay” that can be heard from far distances.
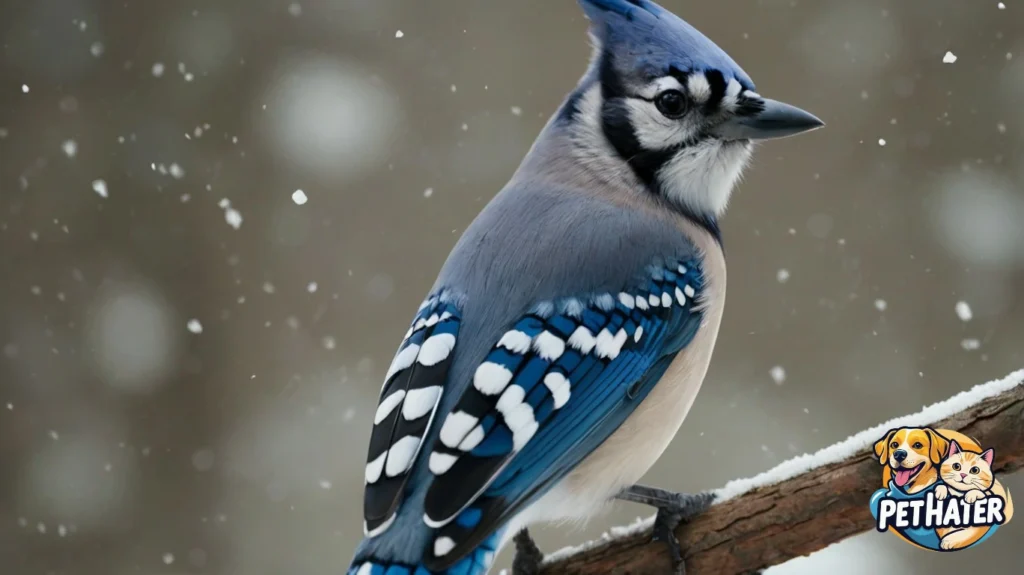

Predators and Threats
Despite their assertive nature, Blue Jays face various predators, especially during the nesting season. Common predators include:
- Snakes
- Raccoons
- Cats
- Hawks and owls
Blue Jays are also vulnerable to habitat loss, pesticide use, and window collisions in urban areas.
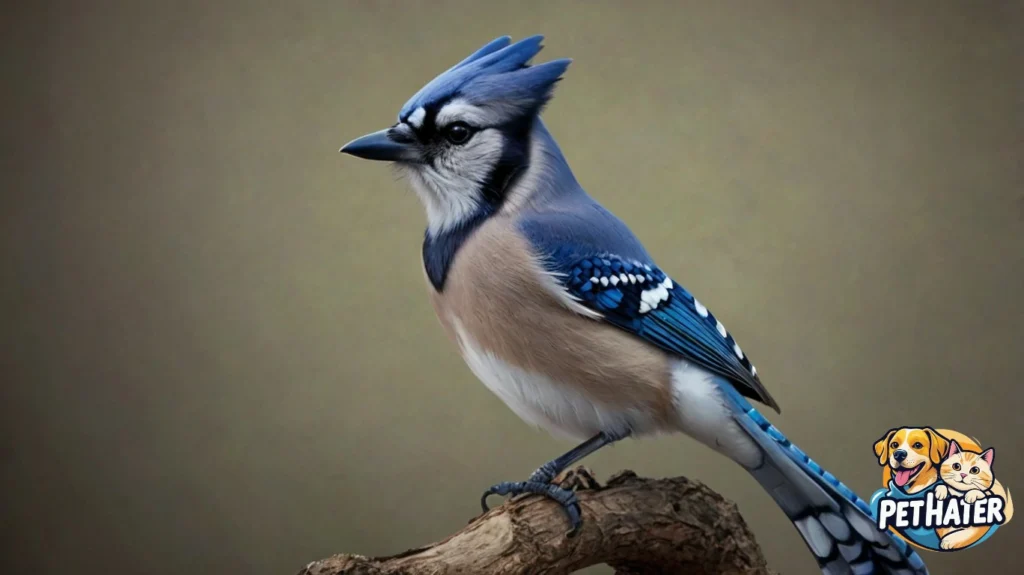

Fun Blue Jay Facts
- Blue Jays can live up to 7 years in the wild and over 15 years in captivity.
- They have been observed using tools, such as using leaves to scoop up food.
- Blue Jays help spread oak trees by burying acorns, some of which are never retrieved and later sprout.
- Their scientific name Cyanocitta cristata translates to “crested blue chatterer.”
How to Attract Blue Jays to Your Backyard
Want to enjoy watching Blue Jays up close? Here are a few tips to bring them to your yard:
- Food: Offer peanuts in the shell, sunflower seeds, corn, or suet in platform feeders or tray-style feeders.
- Water: Provide a bird bath with clean water year-round.
- Shelter: Plant native trees and shrubs to offer natural nesting and hiding spots.
- Avoid pesticides: This keeps their insect food sources safe.
Be patient! Once Blue Jays find a reliable food source, they often return regularly.
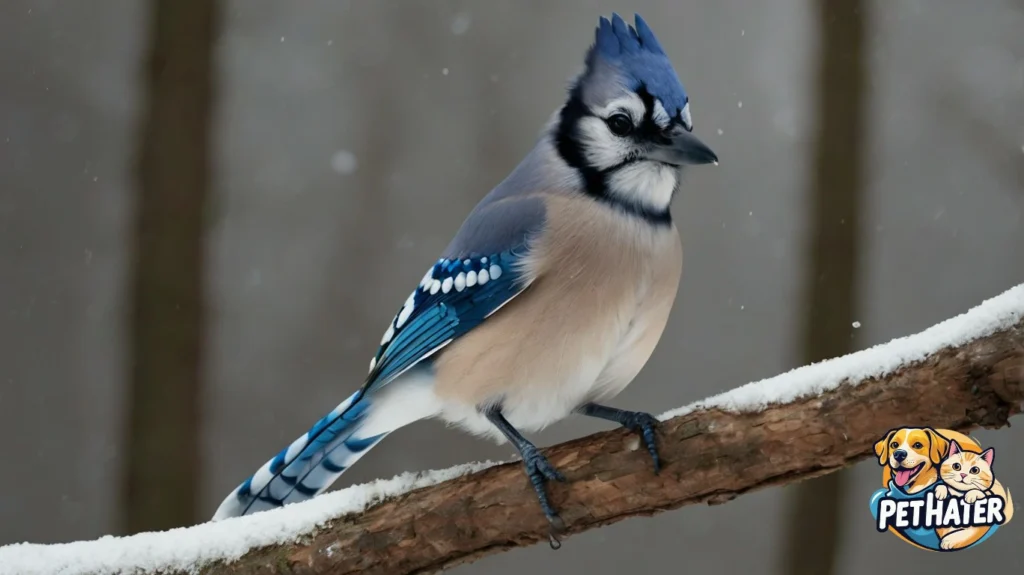

The Role of Blue Jays in the Ecosystem
Blue Jays are not just beautiful birds — they play a vital ecological role. Their habit of caching acorns and other seeds helps promote forest growth and biodiversity. They also help control insect populations by feeding on harmful bugs. Their mimicry and alarm calls can even protect other bird species by alerting them to predators.
Conclusion
The Blue Jay is more than just a pretty bird with a noisy call. It’s a symbol of intelligence, adaptability, and ecological importance. Whether you’re an experienced birder or a casual nature lover, observing Blue Jays can be a rewarding experience. With their complex behaviors, striking appearance, and essential role in forest ecosystems, the Blue Jay truly is one of North America’s avian treasures.